Endoscopic Decompression And Discectomy Surgery
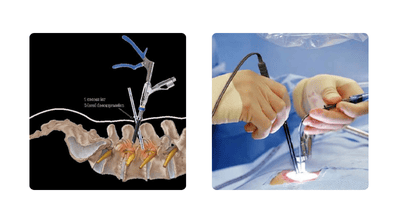
Overview
Endoscopic Decompression Surgery is a minimally invasive surgery that utilizes an endoscopic camera and surgical instruments to access the spine through a very small incision (less than one inch). The procedure allows surgeons to better visualize the disc and nerves of the operational site through a magnified view with the use of a camera and allows direct visualization of the disc and the nerves.
Benefits Of Endoscopic Spinal Decompression Surgery
Some well-recognized benefits of this decompression therapy for the back are as follows:
-
- Minimally invasive, hence minimum blood loss
- Lesser risk involved, Faster recovery from surgery
- Sustained positive results
- Mobility preservation as No hardware placement
- Minimal discomfort
- Small incision hence small scar
- Very effective, especially for sciatica
Indications of Minimally Invasive Endoscopic Spine Surgery
Dr. Sanyam advise this Minimally Invasive Surgery Endoscopic Decompression in the following conditions:
• When conservative methods fail for radicular pain/sciatica or tingling pain, numbness, weakness, pain radiating down to the legs.
• When diagnosed with the condition that will surely require surgery in future
• To preserve spine stability and prevent spine damage
• For treat severe back pain, leg pain, and neurological symptoms
• For conditions like Slip disc/bulging disc, herniated disc, arthritis, stenosis, sciatica pain
Details Of The Endoscopic Micro-Invasive Decompression Surgery
Micro-invasive, endoscopic decompression requires a small incision, usually no larger than 1 cm, and x-rays to gain access to the lumbar spine.
X-ray guidance uses a series of stretch marks to dilate the soft tissue instead of splitting the tissue, allowing the endoscopist to pass through. Specialized instruments can also be used to remove spinal cord tissue with compressed tissue in the density of the. The goal is to remove the nerves in the spinal cord. Depending on the severity of the problem, the patient’s co-morbidities, and the physical characteristics of the patient, the surgery takes about 1-2 hours.
Unlike conventional open surgery, which requires cutting through tissue, muscle and even bone to reach the desired area, endoscopic microdissection uses an endoscope or a small camera to provide the area for microdissection is greater This procedure requires removal of only a small amount of herniated disc compressing the spinal cord.

Trackbacks/Pingbacks